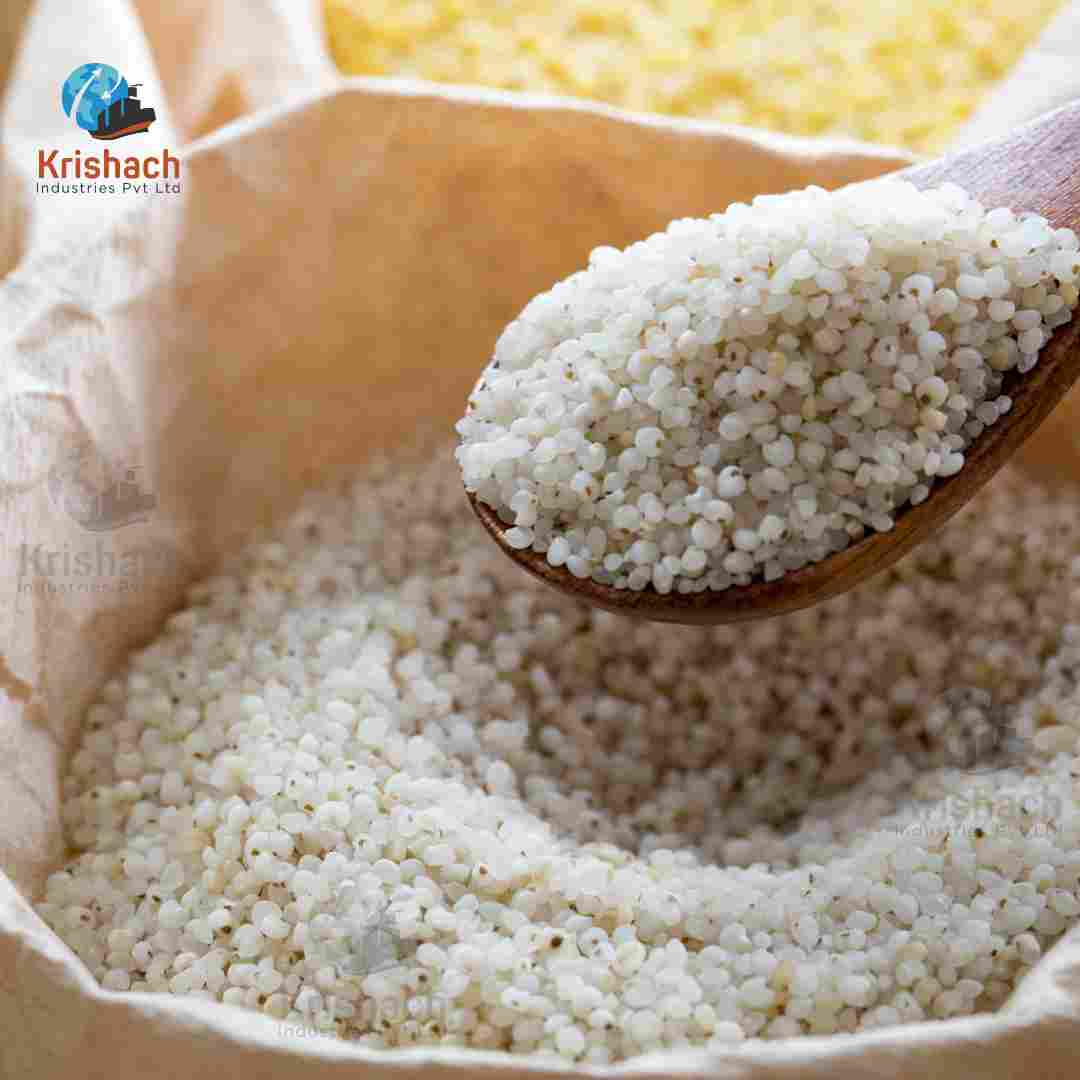
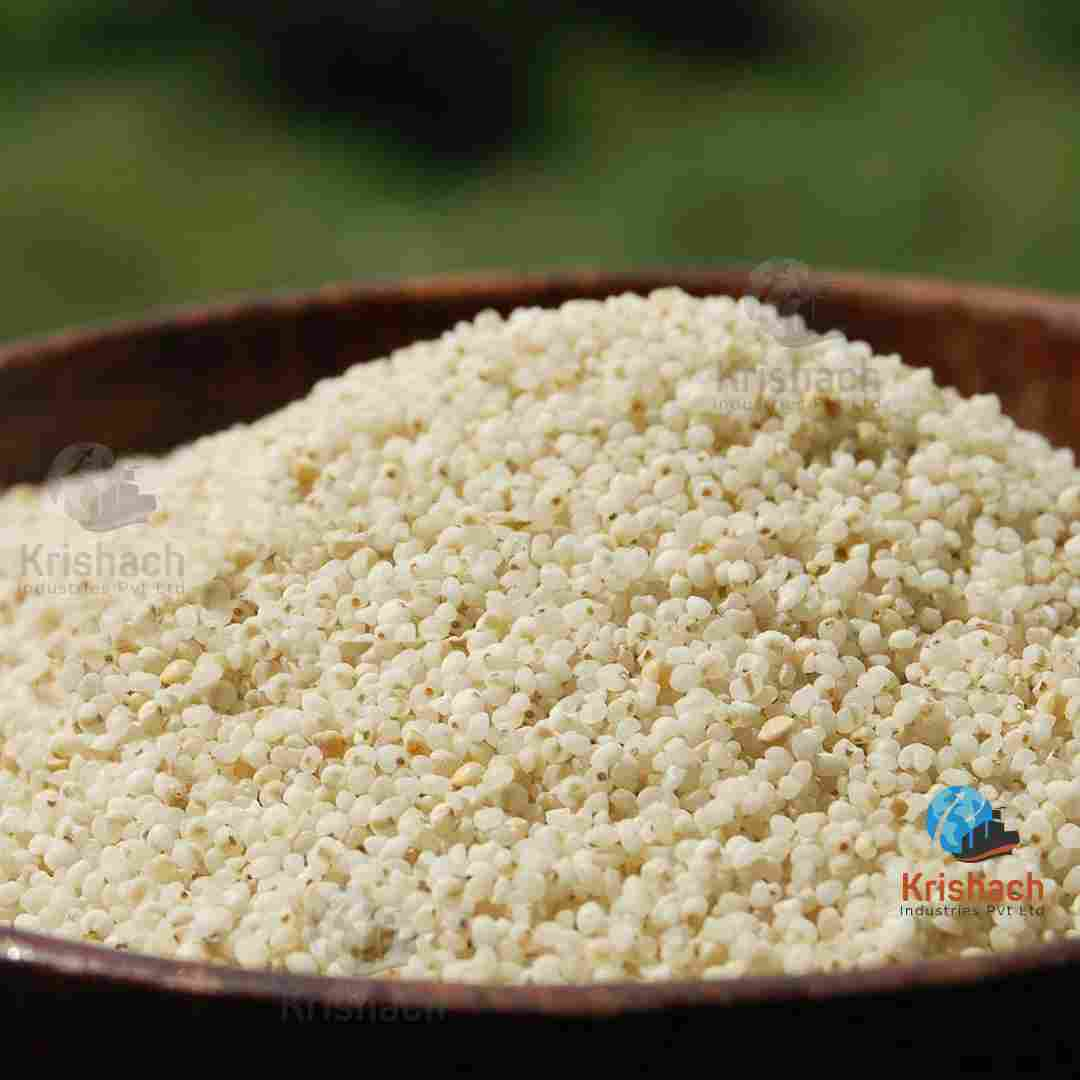
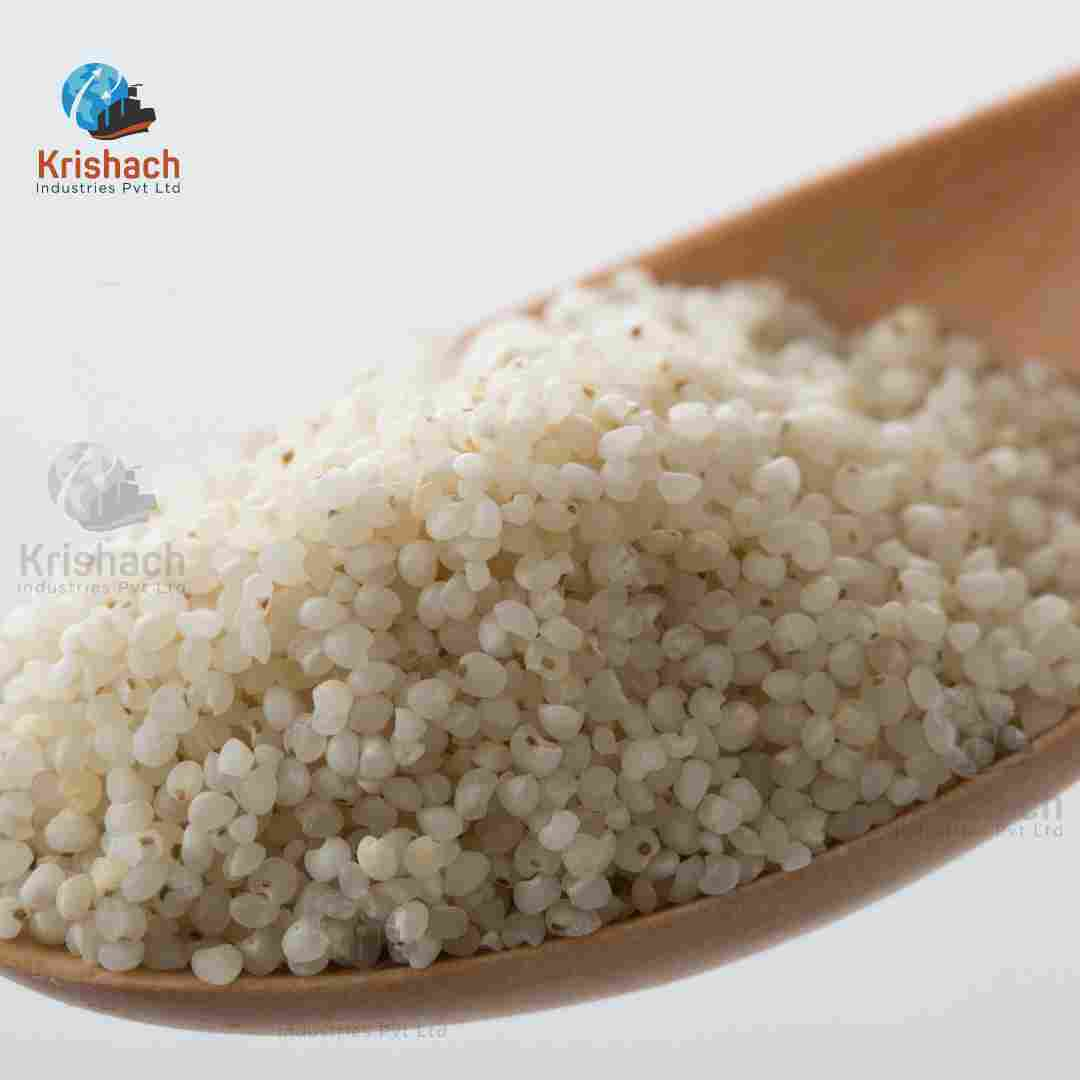
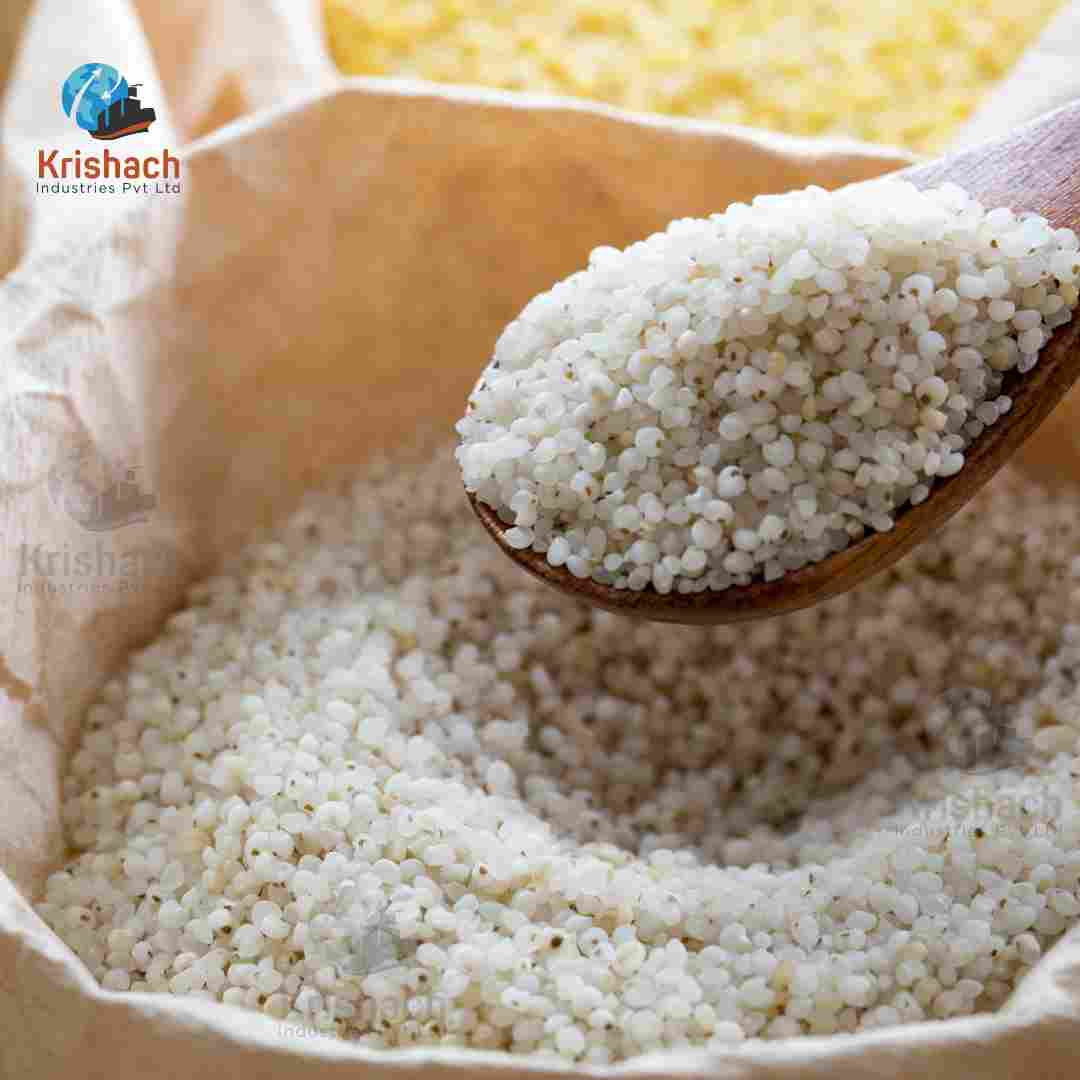
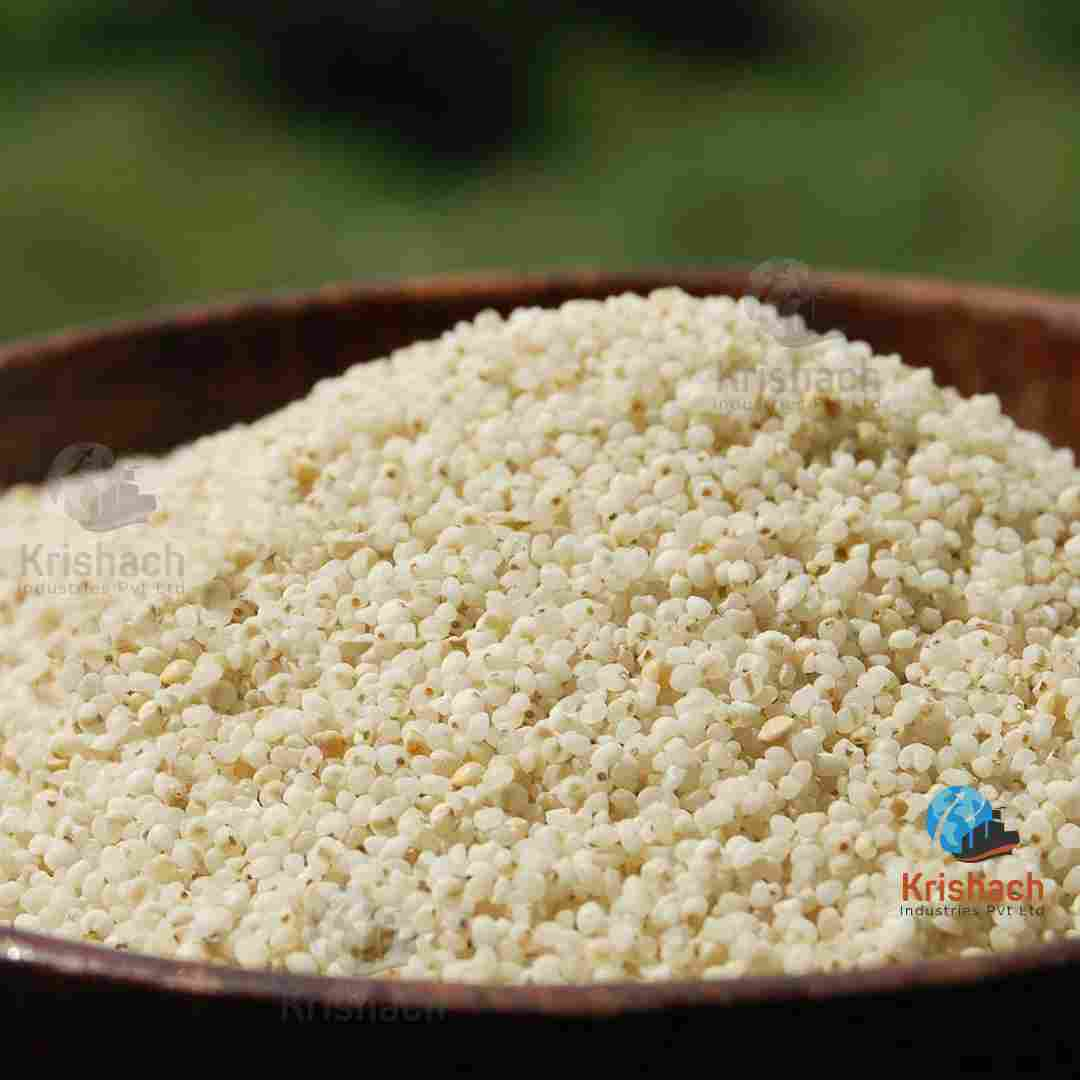
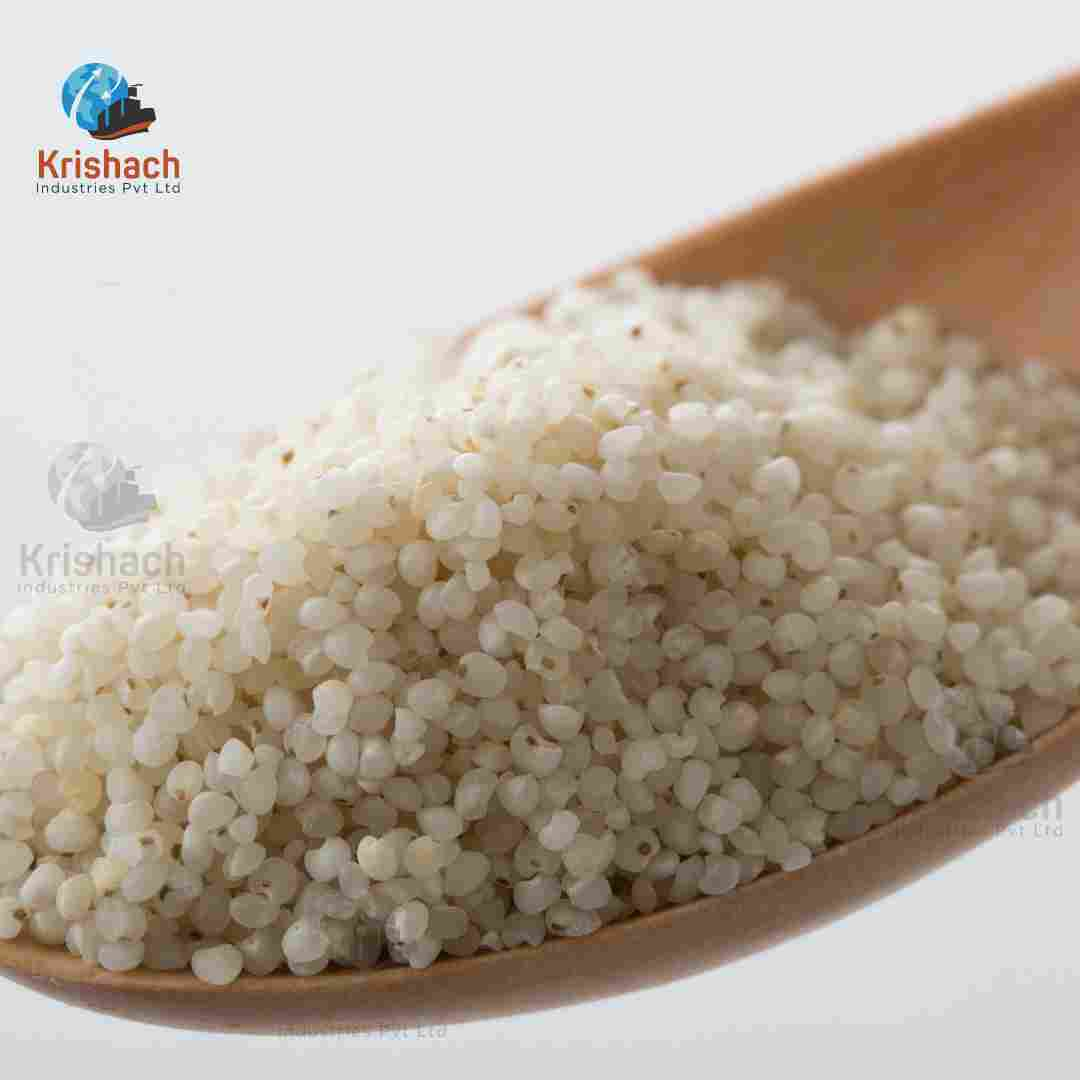
Barnyard Millet, also known as Sanwa, is a small, nutritious grain that belongs to the millet family. It is widely cultivated in India and other Asian countries, particularly in the hilly regions of Uttarakhand, Madhya Pradesh, and Tamil Nadu. Barnyard Millet is known for its rapid growth cycle and ability to thrive in poor soil and drought conditions, making it an important crop for sustainable agriculture.
Key Characteristics:
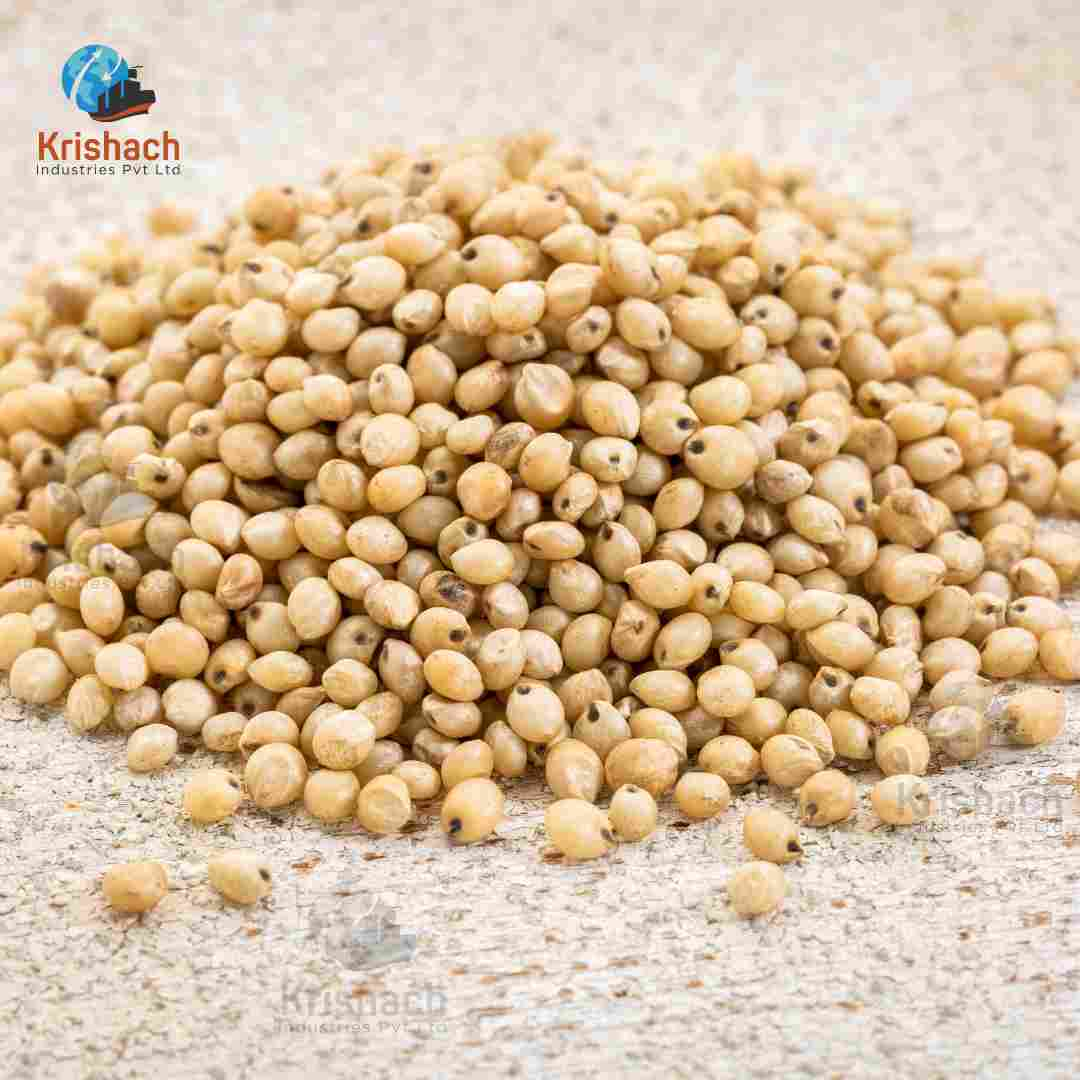
Appearance: Barnyard Millet grains are tiny, oval-shaped, and light brown to whitish in color. They are smaller than most other millet varieties.
Size: The grains are typically about 1-1.5 mm in diameter.
Texture: When cooked, Barnyard Millet has a soft and fluffy texture, similar to broken rice or couscous.
Aroma: The grain has a subtle, earthy aroma that becomes more noticeable when cooked.
Flavors: The flavour of Barnyard Millet is mild and slightly nutty, making it a versatile ingredient that can be used in both sweet and savoury dishes
Specification:
Uses:
Food Products: Barnyard Millet can be used in a variety of culinary applications:
Rice Substitute: It can be cooked and used as a substitute for rice in dishes such as pulao, khichdi, or as a side dish.
Porridge: It is commonly used to make porridge, which is often consumed as a healthy breakfast option.
Baking: Ground into flour, Barnyard Millet can be used in baking breads, pancakes, and cookies.
Traditional Dishes: In India, it is often used to prepare traditional dishes like kheer (sweet pudding), dosa, and idli.
Animal Feed: Barnyard Millet is also used as fodder for livestock due to its nutritional value.
Health Benefits: Known for being light on the stomach and easy to digest, Barnyard Millet is often included in diets aimed at detoxification or weight management.
The high nutritional value, versatility, and adaptability of Barnyard Millet make it an important grain for both dietary and agricultural purposes, contributing to food security and sustainable farming practices.
Benefits:
Barnyard millet is rich in fiber, protein, vitamins, and minerals. It offers numerous health benefits, including aiding digestion, supporting heart health, and regulating blood sugar levels.
Cultivate Seasons for India:
Barnyard millet is typically cultivated during the kharif season in India, with sowing usually done in June-July and harvesting in October-November.
Our Services
Reliable Sourcing:
Reliable sourcing of Barnyard Millet (Sanwa) involves partnering with farmers in regions known for high-quality millet cultivation, such as Uttarakhand, Tamil Nadu, and Madhya Pradesh. Focus on sourcing from farmers who practice sustainable and organic farming techniques to ensure that the millet is non-GMO and free from synthetic chemicals. By collaborating directly with farming communities and cooperatives, you ensure a steady supply of Barnyard Millet that meets strict quality standards. Sourcing from regions where the millet is traditionally grown ensures the best soil and climate conditions for optimal grain quality.
Premium Quality Assurance:
Ensuring premium quality for Barnyard Millet requires implementing stringent quality control measures throughout the supply chain. The millet is tested for moisture content, purity, and the absence of contaminants such as pesticides, heavy metals, and microbial agents. Certifications such as ISO, HACCP, FSSAI, and USDA Organic are important to validate that the millet meets international quality and safety standards. Regular quality inspections are conducted to ensure the millet’s nutritional value, size, color, and overall appearance are up to standard, while also ensuring that the millet is free from impurities.
Processing:
The processing of Barnyard Millet (Sanwa) begins with harvesting when the grains are fully mature and sun-dried in the field to reduce moisture content. The millet undergoes mechanical cleaning using air blowers and separators to remove debris like stones and dirt, followed by de-husking to eliminate the outer husk. The grains are then graded and sorted by size and quality using gravity separators and optical sorters to ensure uniformity and remove discolored or damaged grains. After further drying to reduce moisture content below 10%, the millet is packaged in airtight, food-grade containers to preserve freshness. Finally, it is stored in cool, dry conditions until distribution, ensuring the millet retains its nutritional value and quality.
Packaging, Shipping & Delivery
Packaging:
Bags and Pouches:
For Barnyard Millet (Sanwa), high-quality food-grade materials such as laminated multi-layer pouches (made of materials like PET, PE, BOPP, and Aluminum foil) are used. These bags are moisture-proof and help retain the freshness, flavor, and aroma of the spices. Zip-lock pouches, stand-up pouches, and resealable bags are also popular for smaller quantities.
Polypropylene (PP) Woven Bags:
These are the most common types of bags used for packaging large quantities (25 kg and 40 kg) of Barnyard Millet (Sanwa). They are made of woven polypropylene material, which is strong, lightweight, and durable, providing excellent resistance to tearing and damage during handling and transport.
Laminated Bags:
For additional protection against moisture and humidity, PP woven bags can be laminated with a layer of plastic film. This lamination creates a barrier against moisture, ensuring the spices stay dry and fresh during transportation and storage.
Multi-Wall Paper Bags:
These bags consist of several layers of kraft paper, which provide strength and are often lined with a plastic or polyethylene layer to offer protection against moisture and humidity. They are environmentally friendly and widely used in many markets for exporting food products.
Vacuum-Sealed Packaging:
This type of packaging removes air from the package before sealing, which helps prevent oxidation and moisture build-up, preserving the quality and extending the shelf life of the spices.
Paper or Carton Boxes:
After the packaging, the smaller bags or pouches are placed in corrugated cardboard cartons or paper boxes. These cartons are sturdy, stackable, and protect the contents from physical damage during handling and transportation.
Palletization and Wrapping:
Cartons or sacks are often stacked on wooden or plastic pallets and wrapped with stretch film or shrink wrap. This provides stability, reduces the risk of damage during transport, and makes handling more efficient.
Export Documentation:
Handle all necessary export documentation, including phytosanitary certificates, certificates of origin, and any specific certifications required by the importing country.
Efficient Shipping:
Partner with reliable freight forwarders and logistics companies to ensure timely and safe delivery of goods. Offer multiple shipping options (air, sea, or land) based on customer preferences.