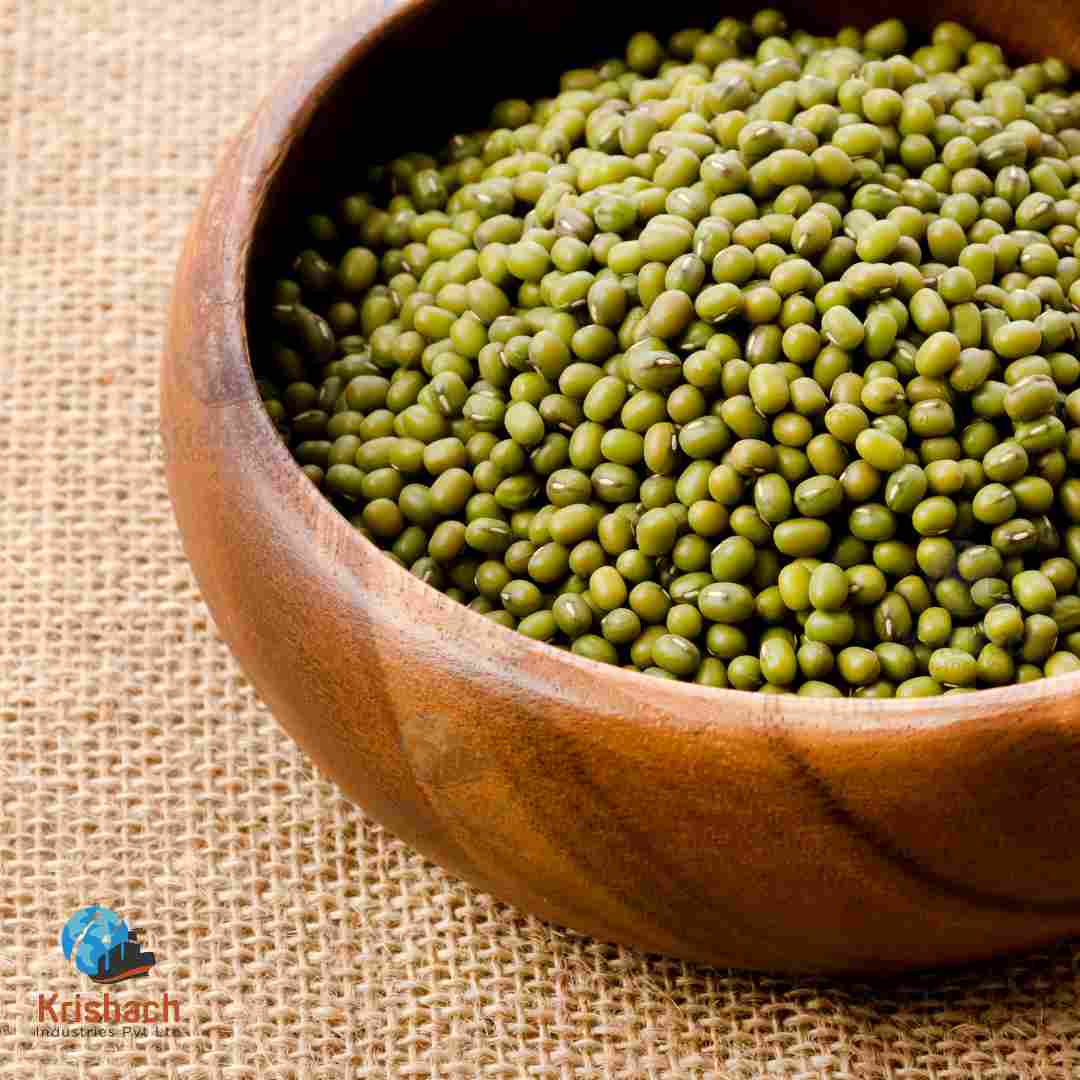
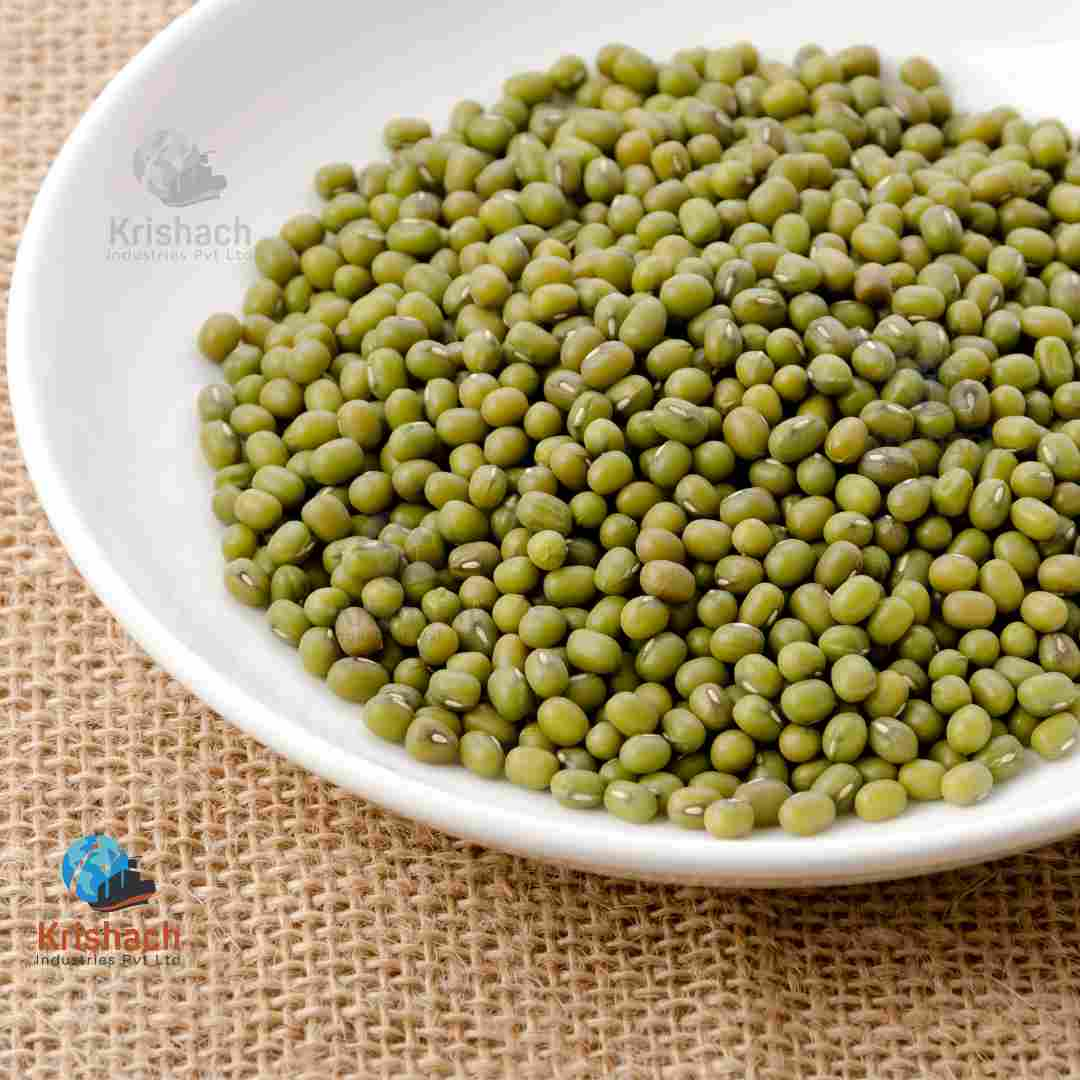
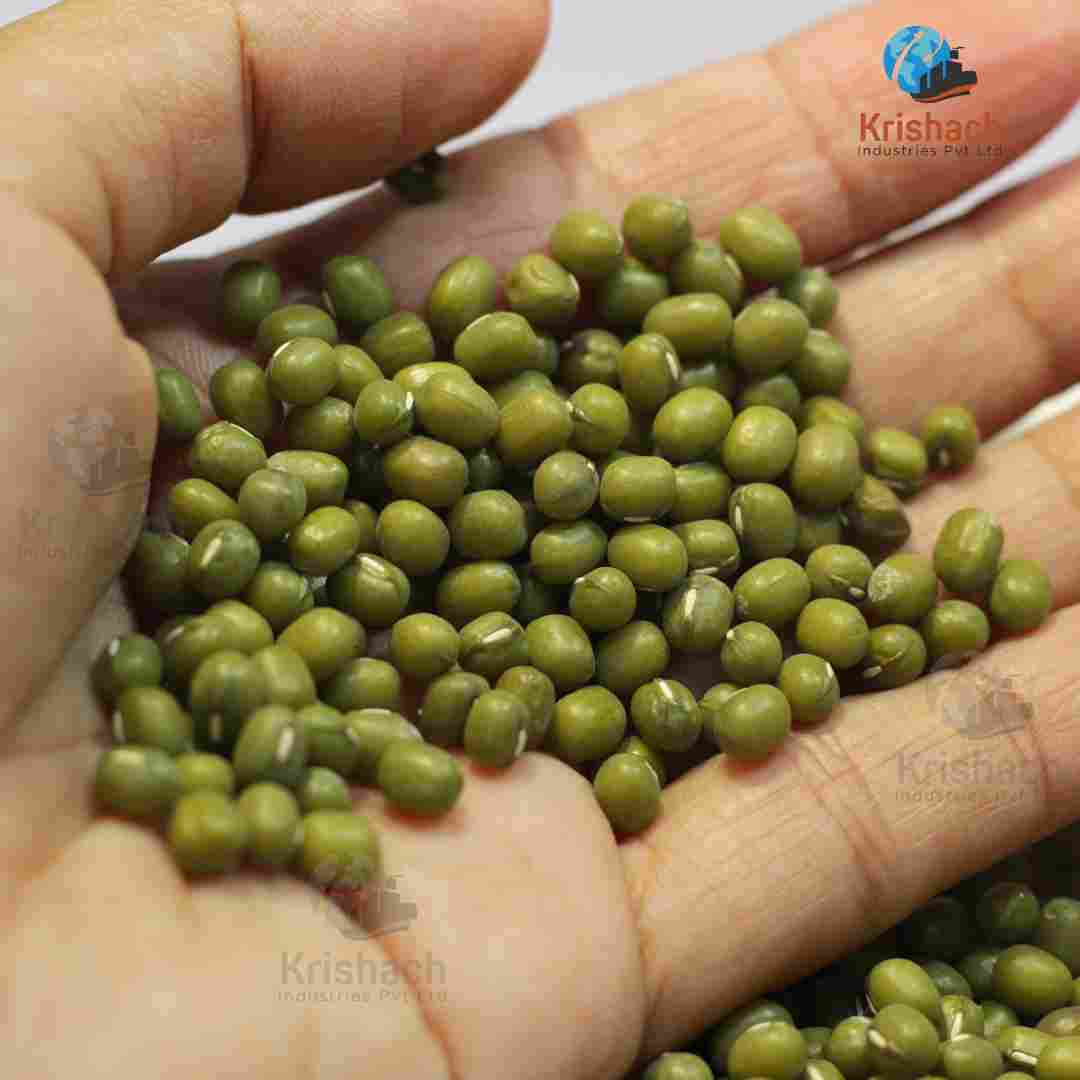
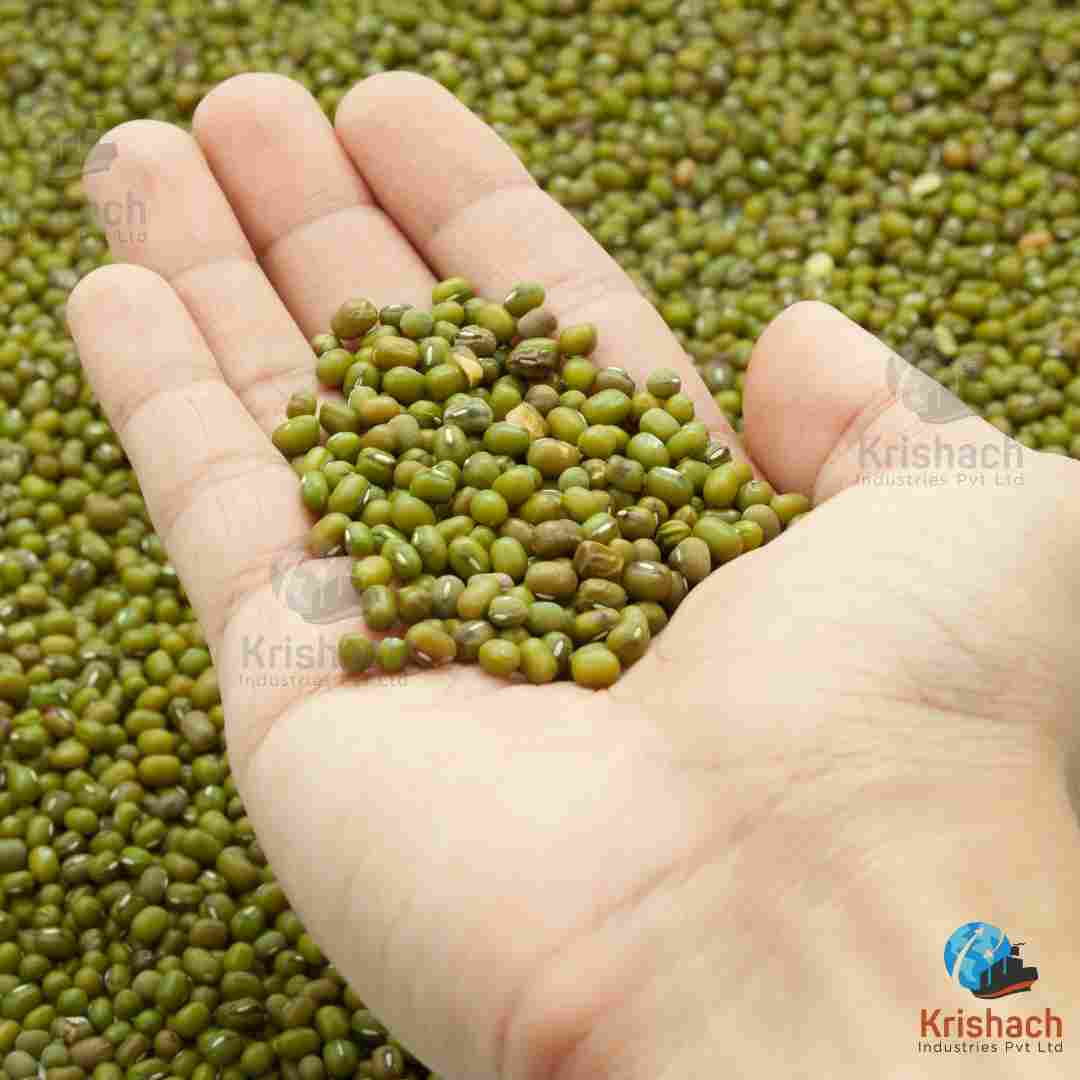
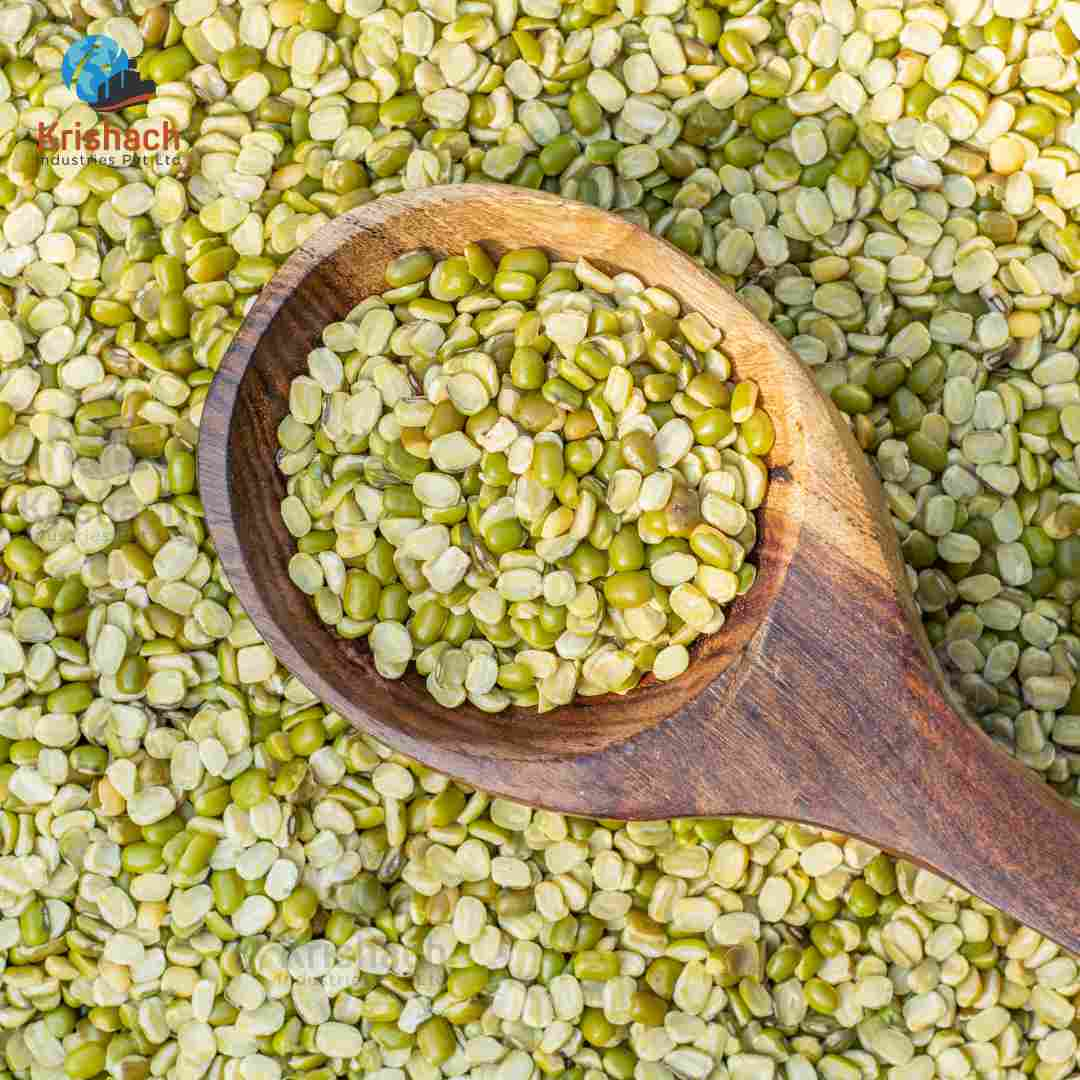
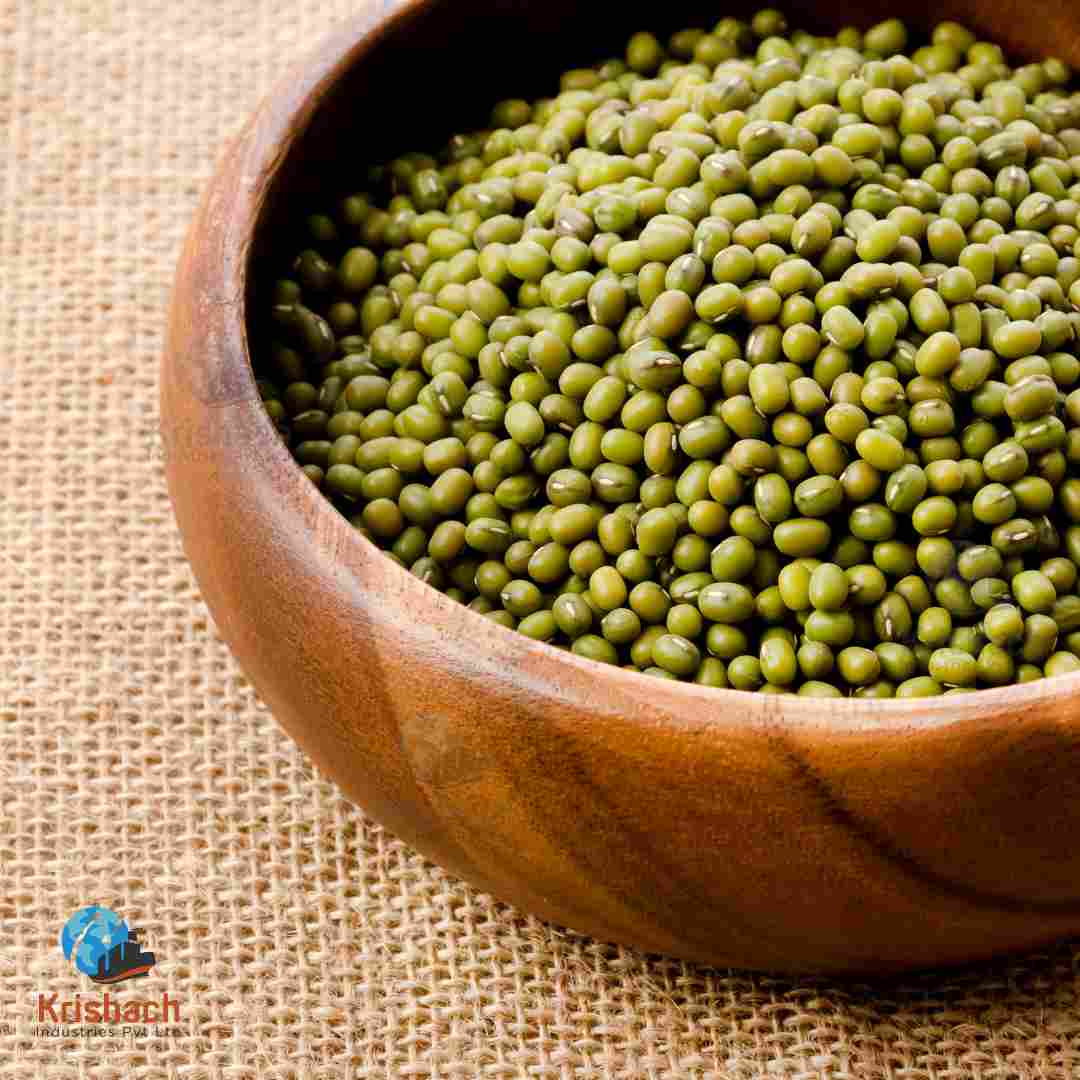
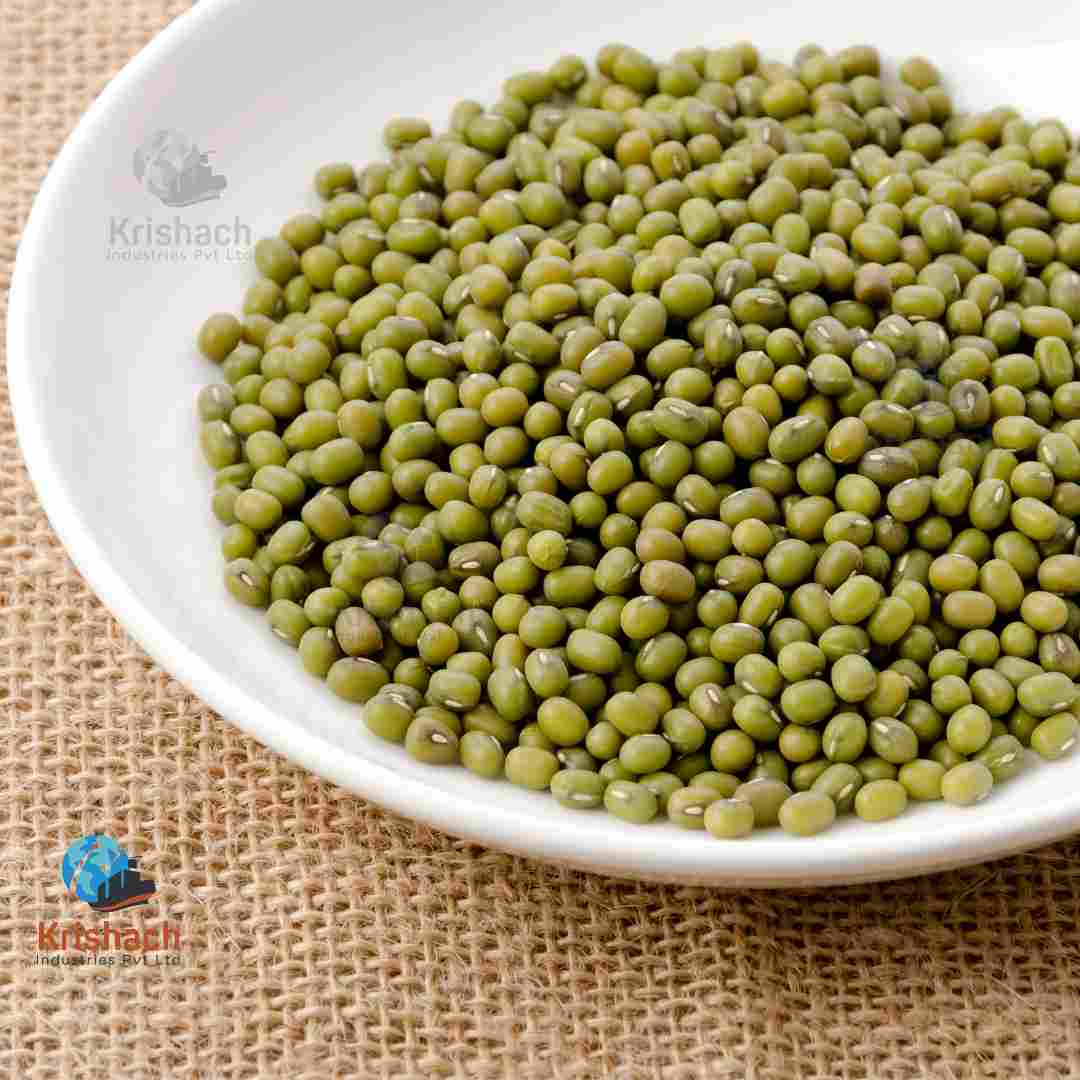
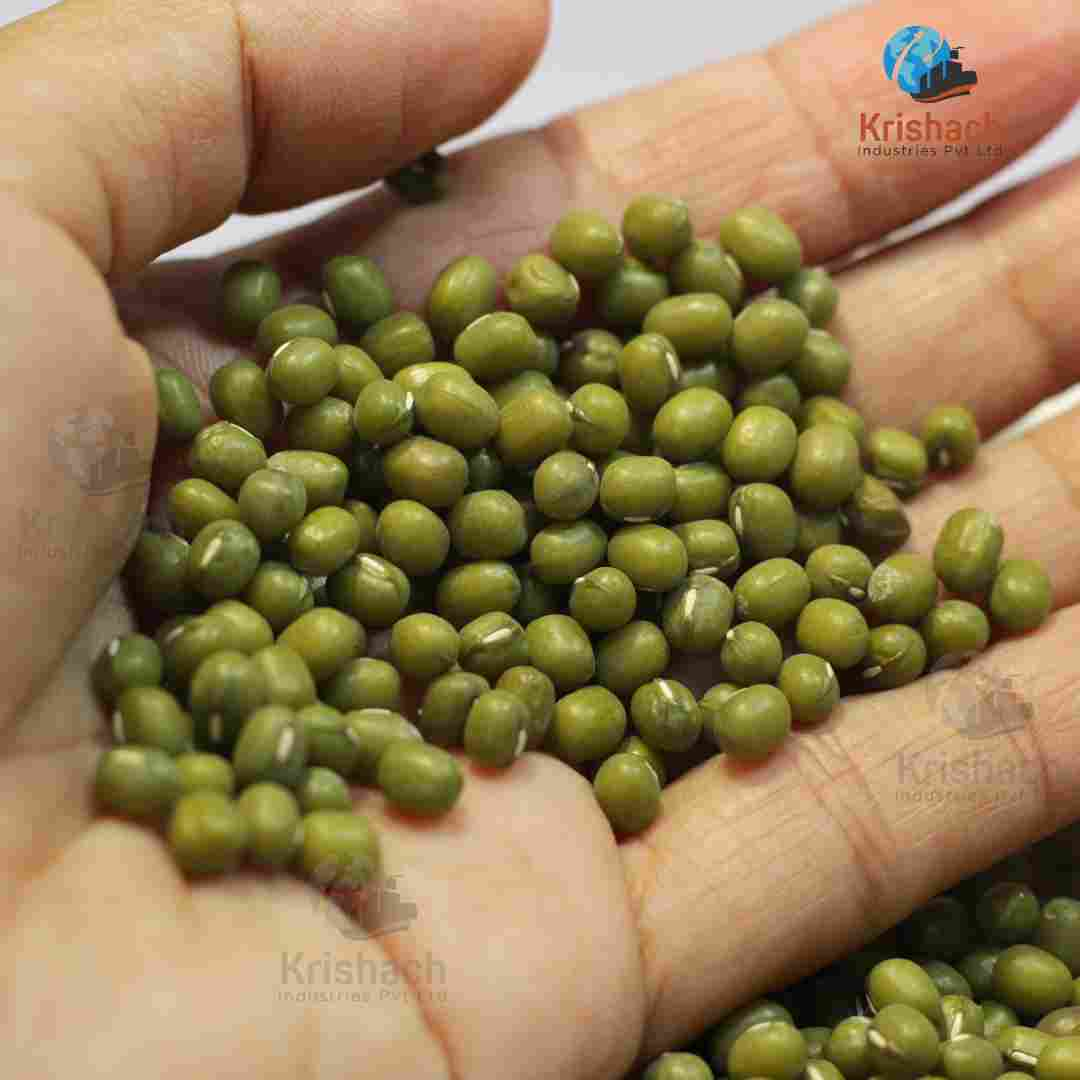
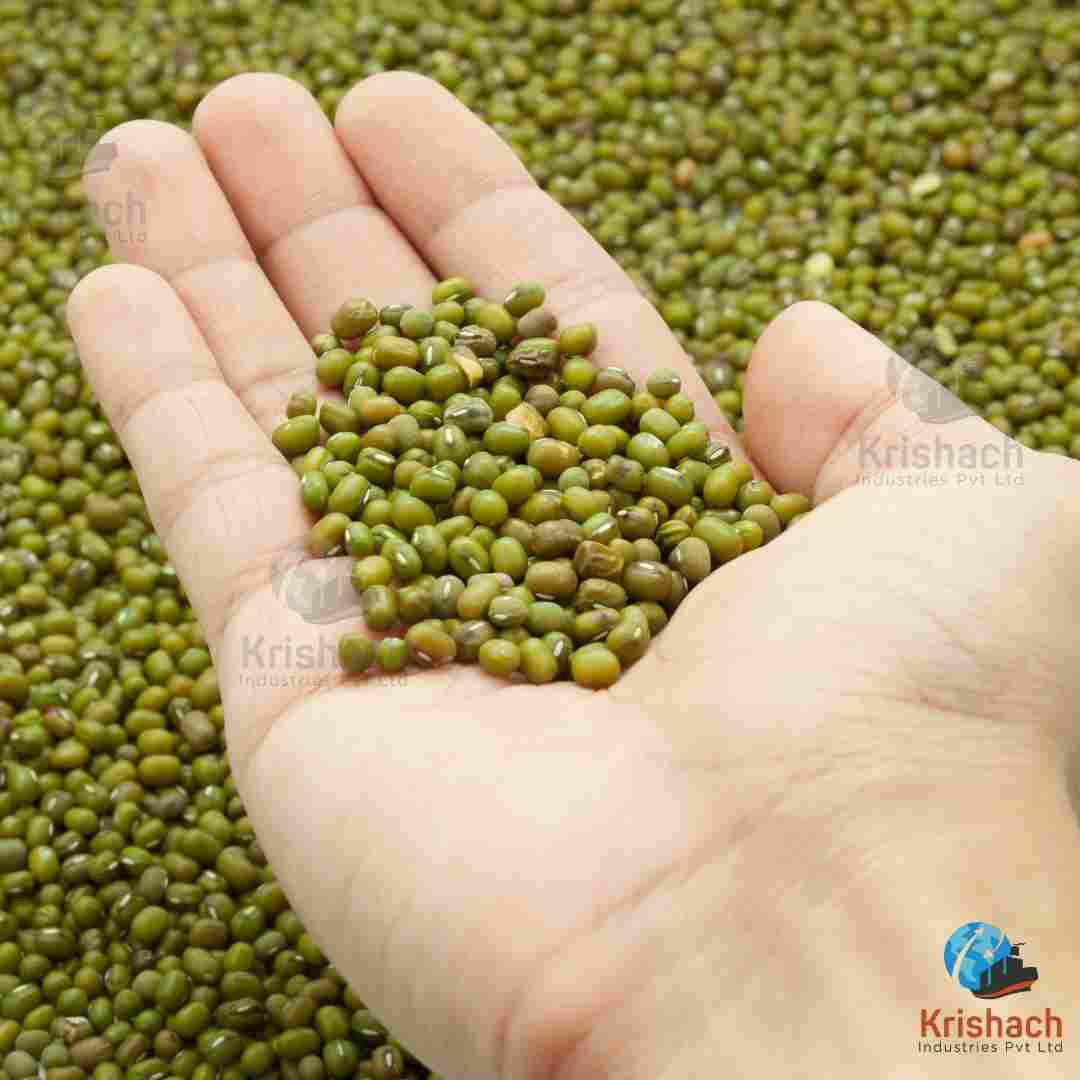
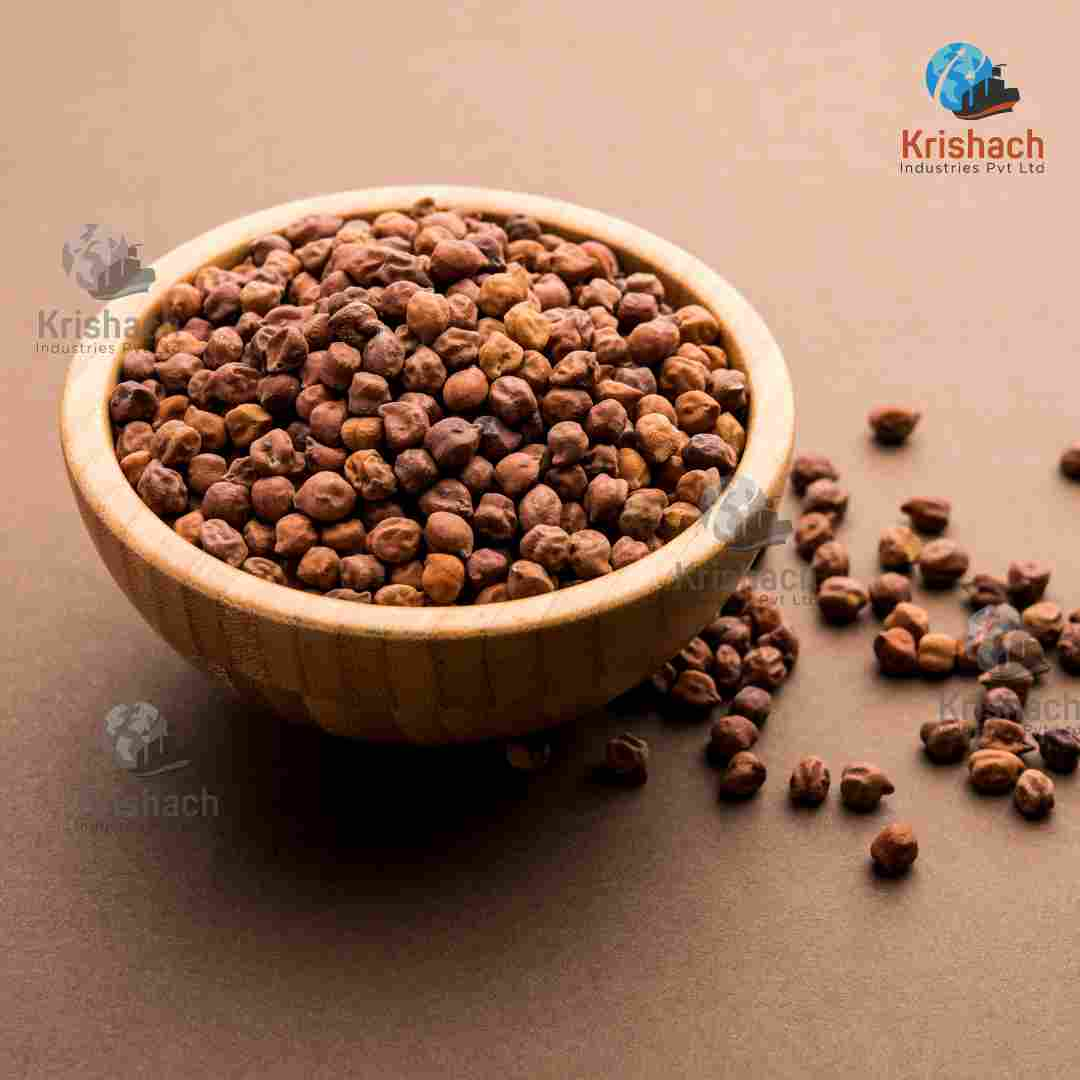
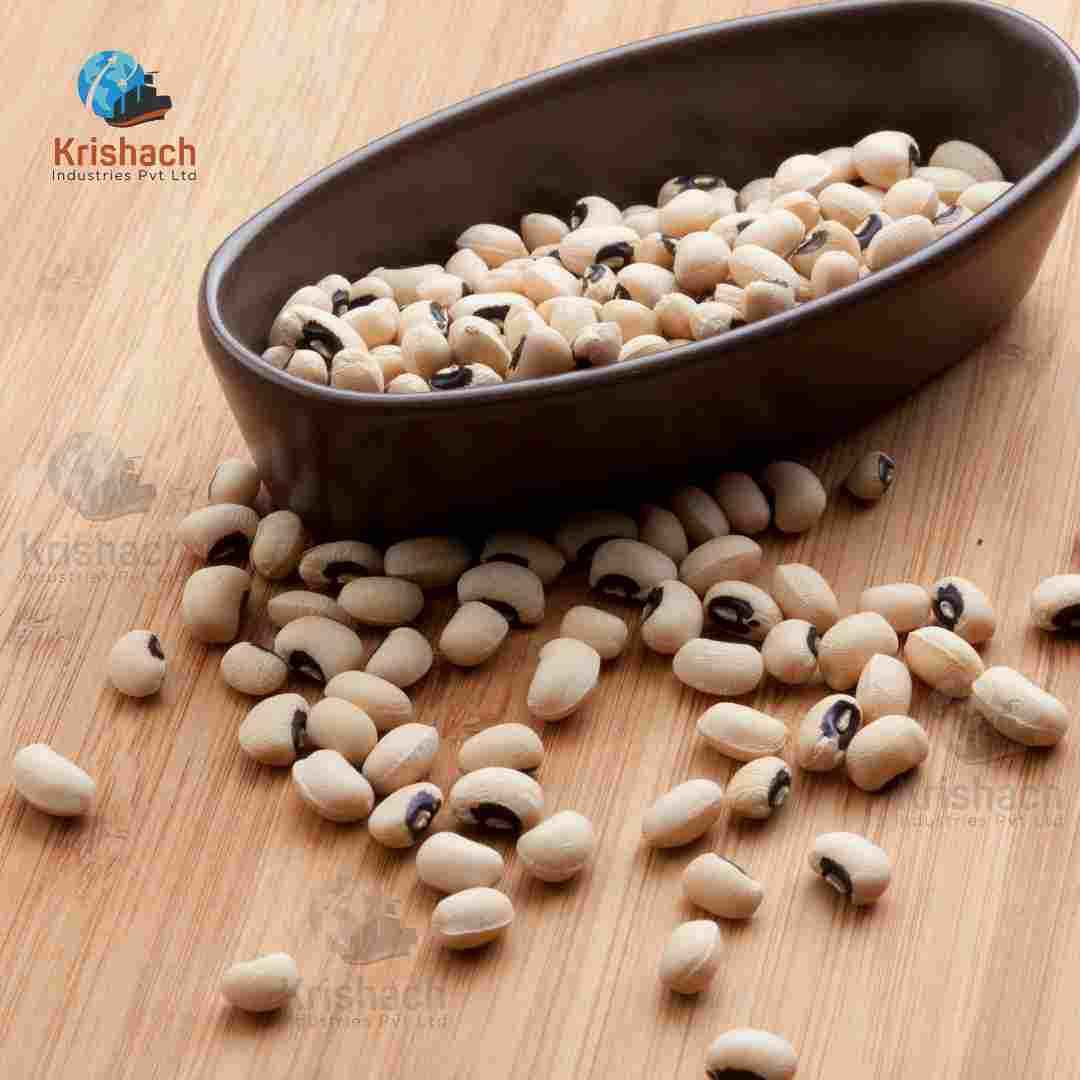
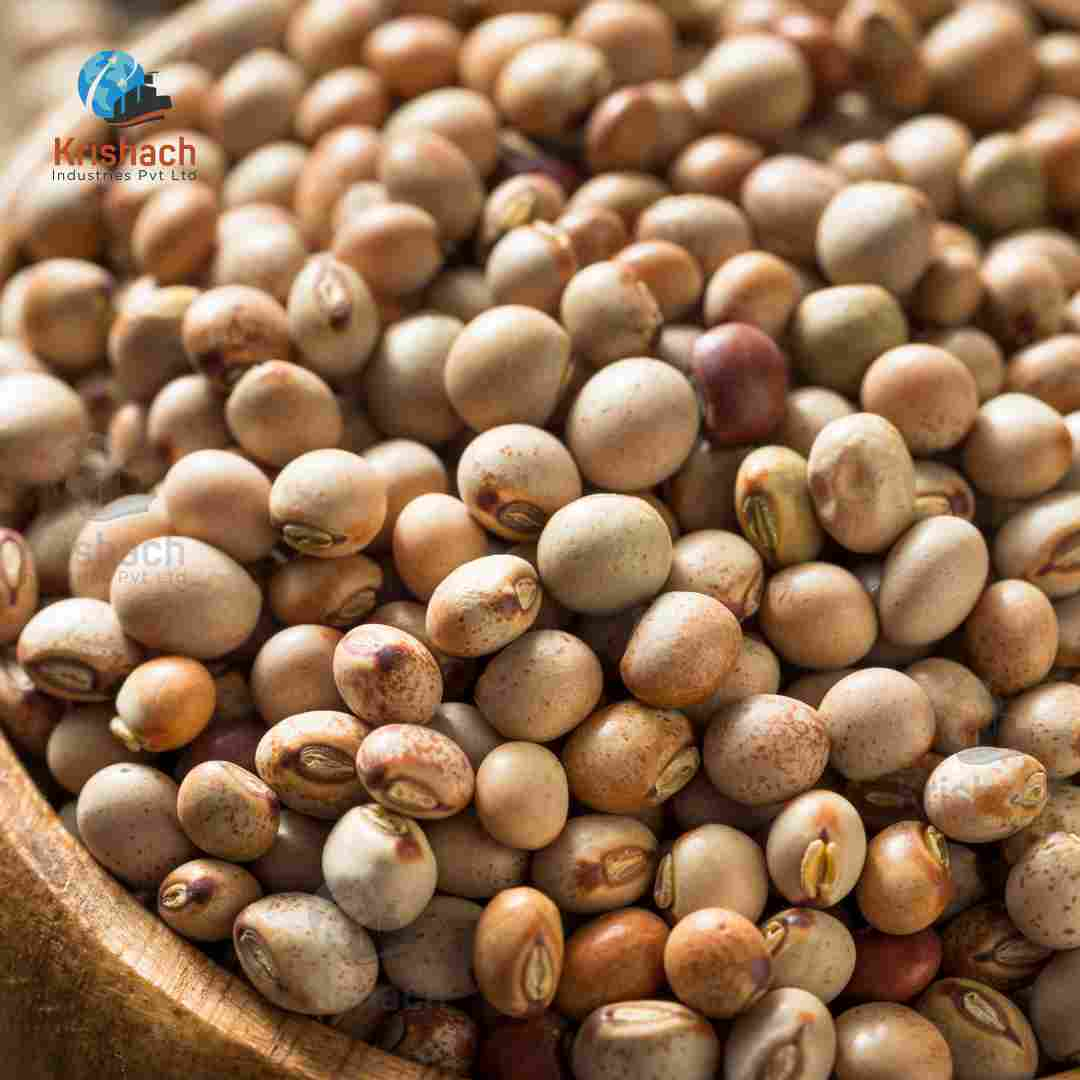
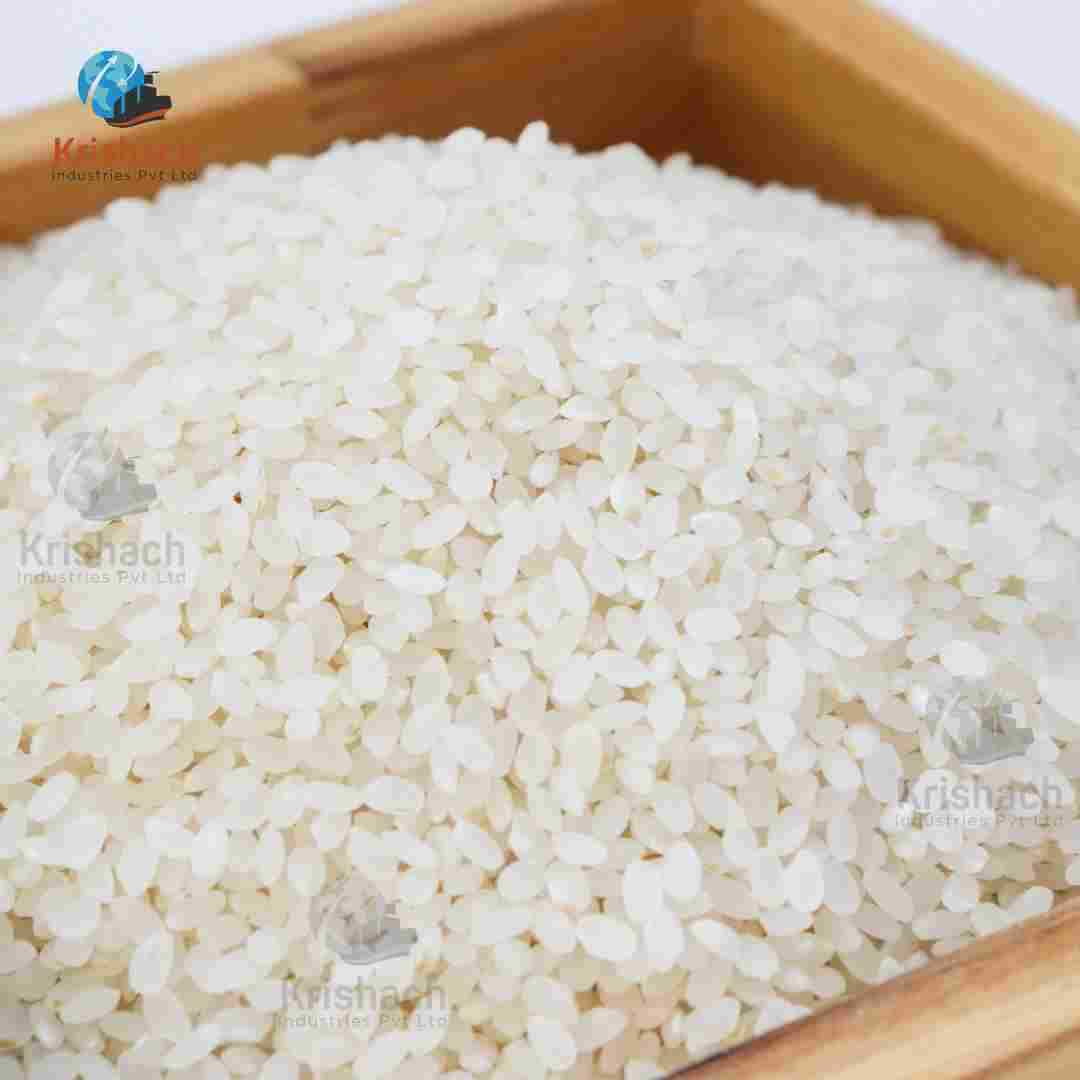
Green gram beans, commonly known as Mung Beans (Vigna radiata), are small, green legumes that have been cultivated for thousands of years in Asia. They are highly valued for their rich nutritional profile, versatility in cooking, and easy digestibility. Mung beans are a staple in many Asian cuisines and are used in a wide range of dishes, from Savory to sweet.
Key Characteristics of Green Gram Beans (Mung Beans):
Appearance:
Shape: Small, oval-shaped beans with a smooth surface.
Size: Approximately 3-4 mm in diameter.
Color: Bright green with a shiny outer skin. Some varieties may have a slightly yellowish tint.
Texture:
Raw: Hard and dense when dried.
Cooked: When boiled or steamed, mung beans become soft, creamy, and slightly mushy while still holding their shape, depending on cooking time.
Aroma: Mung beans have a neutral, slightly earthy smell when raw. When cooked, they release a mild, nutty aroma.
Flavor: Mung beans have a mild, slightly sweet, and nutty flavor. Their subtle taste allows them to complement a variety of flavors in both savory and sweet dishes.
Specification:
Culinary Uses:
Whole Beans: Used in soups, stews, salads, and curries. They are commonly sprouted for use in fresh salads or stir-fries.
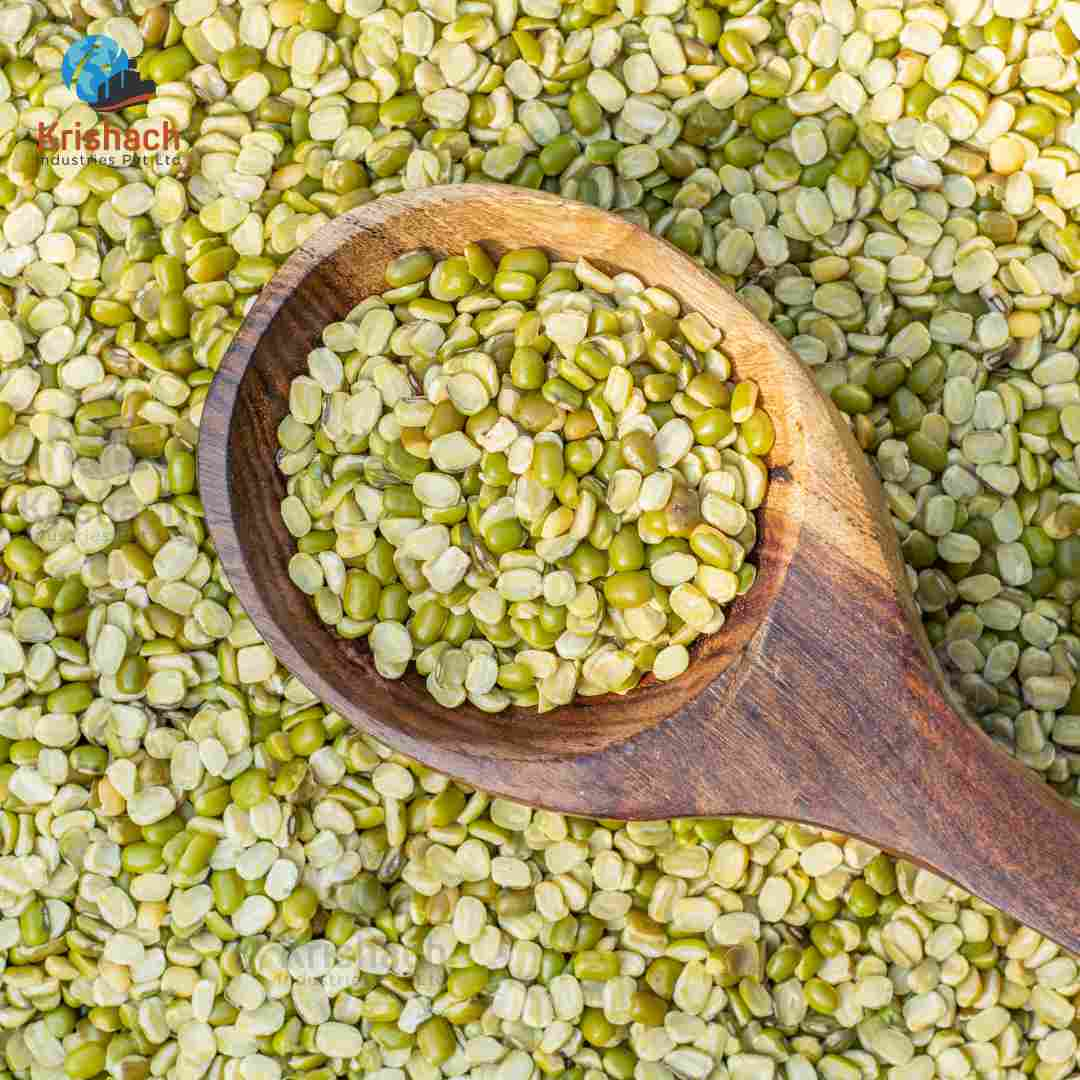
Split Mung Beans (Moong Dal): Hulled and split mung beans are used in Indian dals, soups, and desserts.
Flour: Mung bean flour is used to make noodles, pancakes, and baked goods in various Asian cuisines.
Desserts: In Southeast Asia, mung beans are used in sweet dishes like porridge, mooncakes, and sweet soups.
Nutritional Value: Mung beans are an excellent source of plant-based protein, fiber, vitamins, and minerals, including folate, magnesium, potassium, and iron. They are low in fat and cholesterol-free. Mung beans are also rich in antioxidants and are known for their anti-inflammatory properties. Their high fiber content aids digestion and promotes gut health.
Varieties:
Whole Mung Beans: Used in cooking or sprouting.
Moong Dal (Split Mung Beans): Used in Indian dals, soups, and light curries.
Sprouted Mung Beans: Used in fresh salads, sandwiches, and stir-fry dishes.
Benefits:
Green gram beans are rich in protein, fiber, vitamins, and minerals. They offer numerous health benefits, including aiding digestion, promoting weight loss, and regulating blood sugar levels.
Cultivate Seasons for India:
Green gram beans are typically cultivated during the kharif season in India, with sowing usually done in June-July and harvesting in October-November.
Our Services
Reliable Sourcing:
Reliable sourcing of green gram beans (mung beans) in India begins by partnering with farmers and suppliers from regions known for producing high-quality mung beans, such as Rajasthan, Maharashtra, Andhra Pradesh, and Karnataka. These regions provide the ideal soil, temperature, and rainfall conditions necessary for cultivating nutrient-rich mung beans. Suppliers who follow Good Agricultural Practices (GAP) and employ organic farming methods ensure that the beans are grown without synthetic fertilizers or pesticides. Collaborating with certified suppliers guarantees that the mung beans are harvested at peak maturity to retain their nutritional value and flavor. Traceability and transparency in the supply chain are critical, ensuring sustainable and ethical sourcing from farm to market.
Premium Quality Assurance:
To maintain premium quality, green gram beans undergo rigorous quality checks throughout the supply chain. The first step is testing for size, color, and uniformity, ensuring the beans meet industry standards. Moisture content is carefully monitored to keep it below 12%, preventing spoilage during storage and transportation. The beans are also tested for contaminants like pesticides, heavy metals, and microbial agents. Quality assessments also include checking the beans for purity and cleanliness, with strict standards applied to remove any foreign matter, damaged, or discolored beans. Proper storage facilities, such as temperature-controlled warehouses, help prevent moisture buildup, insect infestation, and mold growth. Certification from ISO, HACCP, and FSSAI ensures adherence to global food safety and quality standards.
Processes:
The processing of green gram beans begins with harvesting at optimal maturity to ensure maximum nutritional benefits. After harvest, the beans are thoroughly cleaned using mechanical cleaners to remove dirt, stones, and foreign material. Next, the beans are sorted by size, color, and quality, discarding any damaged or undersized beans. In some cases, mung beans are dehulled and split to produce moong dal, used in various culinary applications. After sorting, the beans are dried to the appropriate moisture content, followed by grading based on size and quality. Throughout the process, the beans undergo several rounds of inspection for contaminants and quality assurance. Finally, the mung beans are packed in food-grade, airtight packaging to maintain freshness and are stored in cool, dry conditions before distribution. This ensures that the green gram beans retain their natural color, flavor, and nutritional integrity until they reach the consumer.
Packaging, Shipping & Delivery
Packaging:
Bags and Pouches:
For Green Gram Beans (Mung Beans), high-quality food-grade materials such as laminated multi-layer pouches (made of materials like PET, PE, BOPP, and Aluminum foil) are used. These bags are moisture-proof and help retain the freshness, flavor, and aroma of the spices. Zip-lock pouches, stand-up pouches, and resealable bags are also popular for smaller quantities.
Polypropylene (PP) Woven Bags:
These are the most common types of bags used for packaging large quantities (25 kg and 40 kg) of Green Gram Beans (Mung Beans). They are made of woven polypropylene material, which is strong, lightweight, and durable, providing excellent resistance to tearing and damage during handling and transport.
Laminated Bags:
For additional protection against moisture and humidity, PP woven bags can be laminated with a layer of plastic film. This lamination creates a barrier against moisture, ensuring the spices stay dry and fresh during transportation and storage.
Multi-Wall Paper Bags:
These bags consist of several layers of kraft paper, which provide strength and are often lined with a plastic or polyethylene layer to offer protection against moisture and humidity. They are environmentally friendly and widely used in many markets for exporting food products.
Vacuum-Sealed Packaging:
This type of packaging removes air from the package before sealing, which helps prevent oxidation and moisture build-up, preserving the quality and extending the shelf life of the spices.
Paper or Carton Boxes:
After the packaging, the smaller bags or pouches are placed in corrugated cardboard cartons or paper boxes. These cartons are sturdy, stackable, and protect the contents from physical damage during handling and transportation.
Palletization and Wrapping:
Cartons or sacks are often stacked on wooden or plastic pallets and wrapped with stretch film or shrink wrap. This provides stability, reduces the risk of damage during transport, and makes handling more efficient.
Export Documentation:
Handle all necessary export documentation, including phytosanitary certificates, certificates of origin, and any specific certifications required by the importing country.
Efficient Shipping:
Partner with reliable freight forwarders and logistics companies to ensure timely and safe delivery of goods. Offer multiple shipping options (air, sea, or land) based on customer preferences.